Passing parameters to Linux Device Drivers - builtin, modules
In C Programs, we pass command line parameters through argc/argv. Kernel programming also allows us to pass command line parameters.
The command line parameters provides a single linux driver to do multiple things, for example
The command line parameters provides a single linux driver to do multiple things, for example
- instead of fixing to a single I/O address for read/write, it can provide that as command line argument and allow user to read/write any address.
- Enable/disable debug logs/printk
- Allow user to set the mode if the driver supports multiple modes
How to pass Parameters to modules?
We can add parameters using module_param macro. Declared in moduleparam.h file
name: name of the variable
type: Type of the Variable. Supported types are charp, bool, invbool, int, long, short, uint, ulong, ushort
perm: Permissions for the sysfs entry.
E.g. S_IRUGO : Only read by all users
0 : No sysfs entry
You can also use numeric values like 0644 for permission entry.
Sample Program to demonstrate parameter passing
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
char *name = "Embedded";
int loop_count = 1;
module_param(name, charp, S_IRUGO);
module_param(loop_count, int, S_IRUGO);
static int test_arguments_init(void)
{
int i;
printk(KERN_INFO"%s: In init\n", __func__);
printk(KERN_INFO"%s: Loop Count:%d\n", __func__, loop_count);
for (i = 0; i < loop_count; i++)
printk(KERN_INFO"%s: Hi %s\n", __func__, name);
return 0;
}
static void test_arguments_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_INFO"%s: In exit\n", __func__);
}
module_init(test_arguments_init);
module_exit(test_arguments_exit);
How to pass Parameters?
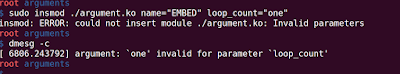
Let's find out what will happen when we pass wrong parameters, if I pass string in loop_count.
It will throw invalid parameter error, and the module is not loaded.
How to find out the values of already loaded modules
$ cat /sys/modules/<module_name>/parameters/<parameter_name>
This is only possible, if the permission field in the module_param macro is not zero.
How can we pass arguments to modules which are builtin?
Module parameters for builtin modules are passed through kernel command line.
Syntax: <module_name>.<parameter_name>=value
So, if the argument module was builtin, we can append argument.loop_count=5 to the kernel command line for passing 5 as loop_count
How can we pass arguments which are called by modprobe?
modprobe reads /etc/modprobe.conf file for parameters.




Comments
Post a Comment