Linux Device Driver Code to print all the loaded modules along with number of exported symbols
Kernel module in Linux is represented by 'struct module'
The module structure is defined in <linux/module.h>
struct module {
enum module_state state;
/* Member of list of modules */
struct list_head list;
/* Unique handle for this module */
char name[MODULE_NAME_LEN];
.....
unsigned int num_syms;
....
};
The above structure has a linked list embedded in it, through which we can traverse to all the modules present in it
Code:
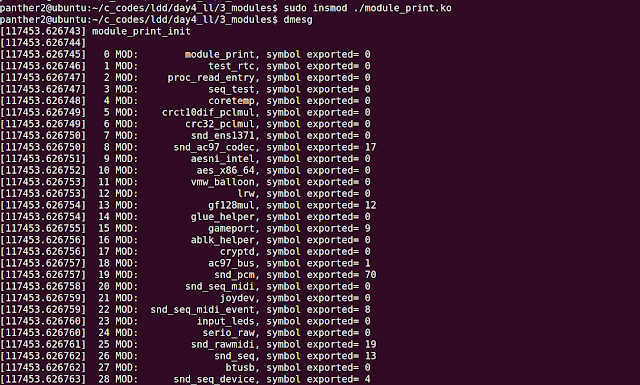
Output:
The module structure is defined in <linux/module.h>
struct module {
enum module_state state;
/* Member of list of modules */
struct list_head list;
/* Unique handle for this module */
char name[MODULE_NAME_LEN];
.....
unsigned int num_syms;
....
};
The above structure has a linked list embedded in it, through which we can traverse to all the modules present in it
Code:
Output:


Comments
Post a Comment