In Linux, Serial Port input can be configured in two ways:
1. Canonical Mode
2. Non-Canonical Mode
Canonical Mode: In canonical mode, read on the serial port will not return until a new line, EOF or EOL character is received by the Linux Kernel. In this more, read will always return an entire line, no matter how many bytes are requested.
Non-Canonical Mode: In non-canonical mode, read on the serial port will not wait until the new line. Number of bytes read depends on the MIN and TIME settings.
MIN: Minimum number of bytes that must be available in the input queue in order for read to return
TIME: How long to wait for input before returning, in units of 0.1 seconds.
|
MIN and TIME
|
Behavior
|
|
MIN = 0, TIME = 0
|
Read
returns immediately with as many characters available in the queue, up to the
number requested. If no characters in the queue, read returns 0
|
|
MIN = 0, TIME > 0
|
Read waits for TIME time for input to
become available, if we receive a single character in the TIME duration, read
returns immediately. It returns as many characters up to the number requested.
If timer expires and there is no receive characters, read returns 0
|
|
MIN > 0, TIME = 0
|
Read waits until at least MIN bytes are
available in the input queue. At the time, read returns as many characters
are available up to the number requested.
|
|
MIN > 0, TIME > 0
|
Read returns until either MIN bytes have
arrived in input queue, or TIME elapses with no further input. read always
block until the first character arrives, even if TIME elapses first.
|
Setting of canonical or non-canonical mode is determined by the ICANON flag in the c_lflag of the struct termios
The MIN and TIME can be set in the c_cc[VMIN], c_cc[VTIME] of the termios structure.
When you open serial port in minicom/cutecom, it configures the input mode to non-canonical mode, you can observe it by running 'stty -F <port> -a' after you opened the port in minicom/cutecom
For this code to work, I connected two PL2303 USB to serial device (TX -> RX, RX->TX)
Note: '\r' is Carriage Return , '\n' is Line Feed
C Code Demonstrating Canonical Mode
canonical_write.c:
canonical_read.c:
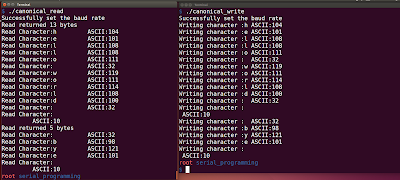
Output
You can observe when you run the code, only when the new line character is transmitted by the write code, the read function returns.
C Code Demonstrating Non-Canonical Mode
non_canonical_write.c
non_canonical_read.c
Output:
You can observe when you run the code, for each two characters transmitted, read returns with data



Whoops, sorry I'm mistaken, you simply swapped the code and the headline :D
ReplyDeleteSeems like my first comment was lost in the void, now this one sounds a bit dumb...
Delete