CLONE_SIGHAND example
This post we will write a code, which will give us an observation what changes when CLONE_SIGHAND is added and when it is removed.
Code:
Output:
Notes:
You can see from the code, when CLONE_SIGHAND was set, parent modifying the default behavior of SIGTERM affected the parent process, and it did not ignore the SIGTERM signal and instead called the signal handler.
Code:
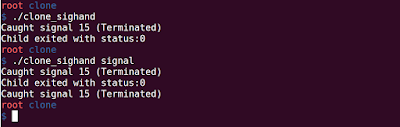
Output:
Notes:
You can see from the code, when CLONE_SIGHAND was set, parent modifying the default behavior of SIGTERM affected the parent process, and it did not ignore the SIGTERM signal and instead called the signal handler.


Comments
Post a Comment