Internals of module_init and module_exit
We know from our hello world device driver program , that on insmod, the function passed in the module_init macro is called, and on rmmod, the argument passed in the module_exit is called.
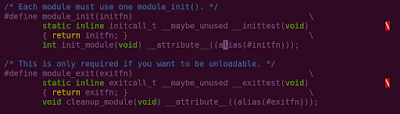
Let's see the definition of this macro, it is present in linux/module.h
The purpose of defining __inittest function is to check during compile time, the function passed to module_init() macro is compatible with the initcall_t type.
initcall_t is defined in linux/init.h:
typedef int (*initcall_t)(void);
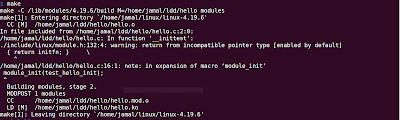
If you declare module_init function which returns void instead of int, the compiler will throw warning:
initcall_t is defined in linux/init.h:
typedef int (*initcall_t)(void);
If you declare module_init function which returns void instead of int, the compiler will throw warning:
Loading this module generated an oops message.
The last line uses the alias attribute of gcc to assign another name to init_module, so that you can have a better name as per your driver (e.g. cdrom_init instead of init_module), instead of each driver having init_module. Same is the case with module_exit, giving whatever name in module_exit as parameter to cleanup_module.
To understand alias attribute, you can refer to my tutorial of alias
Code:
Output:
Notes:
You can see on loading the module with insmod, init_module is called and removing the module with rmmod cleanup_module is called
You can see on loading the module with insmod, init_module is called and removing the module with rmmod cleanup_module is called




Comments
Post a Comment